Miyawaki Forests: A Compact Solution for Urban Reforestation
In an era where rapid urbanization has led to the loss of green spaces and environmental degradation, a unique approach to reforestation has emerged, known as the Miyawaki method. Developed by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, this technique has gained global recognition for its ability to create dense, biodiverse forests in small urban spaces, offering a sustainable solution to combat climate change and restore ecological balance.
What are Miyawaki Forests?
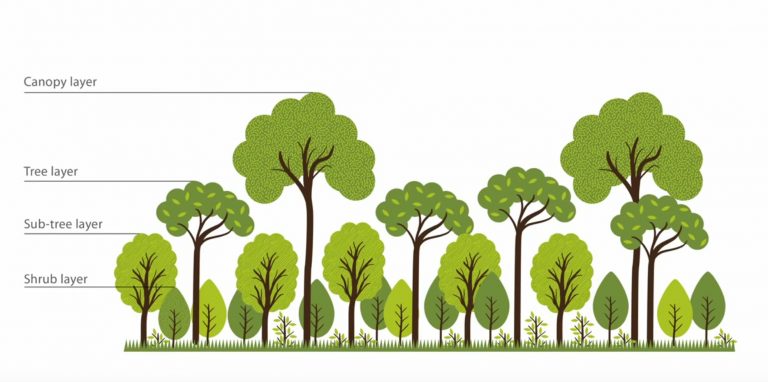
Miyawaki Forests, also referred to as urban tiny forests, are meticulously designed and planted using Miyawaki's unique methodology. These forests are created by carefully selecting and planting a diverse mix of native tree species in a specific pattern, mimicking the natural growth patterns found in ancient forests. The key principles behind Miyawaki's approach include:
- Native Species Selection: Miyawaki emphasizes the use of native tree species that are well-adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, ensuring their survival and promoting biodiversity.
- Dense Planting: Trees are planted in a dense, multi-layered pattern, with different species occupying different vertical strata, replicating the structure of natural forests.
- Soil Preparation: Appropriate soil preparation techniques are employed, including the addition of nutrient-rich biomass, to create an ideal environment for rapid growth and nutrient cycling.
- Minimal Maintenance: Once established, Miyawaki Forests require minimal maintenance, relying on natural processes for self-sustenance and resilience.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests
- Rapid Growth: These forests grow at an astonishing rate, achieving in years what would typically take decades in traditional reforestation methods. This rapid growth is facilitated by the dense planting and soil preparation techniques.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: By incorporating a diverse mix of native species, Miyawaki Forests create rich habitats that support a wide range of flora and fauna, contributing to the conservation of local biodiversity.
- Carbon Sequestration: The dense vegetation and rapid growth of Miyawaki Forests make them highly effective carbon sinks, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change by absorbing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- Urban Heat Island Mitigation: The canopy coverage and evapotranspiration from these forests help to regulate urban temperatures, reducing the urban heat island effect and improving air quality.
- Noise Reduction: The dense vegetation acts as a natural barrier, absorbing and deflecting sound waves, contributing to a quieter urban environment.
- Aesthetic and Recreational Value: Miyawaki Forests provide green spaces within urban areas, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and offering opportunities for recreation, education, and community engagement.
Global Adoption and Success Stories
The Miyawaki method has gained widespread recognition and adoption worldwide, with successful implementations in various urban centers. For example, in India, the city of Hyderabad has embraced the concept, establishing numerous Miyawaki Forests within its metropolitan area. These forests not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also serve as community hubs, fostering environmental awareness and public engagement.
Similarly, in the Netherlands, the city of Utrecht has implemented Miyawaki Forests as part of its urban greening strategy, transforming underutilized spaces into thriving ecosystems and promoting biodiversity conservation.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Miyawaki method offers numerous advantages, it is important to consider potential challenges and limitations. These may include:
- Land Availability: Finding suitable land in densely populated urban areas can be a challenge, necessitating innovative approaches such as utilizing vacant lots, rooftops, or reclaimed brownfield sites.
- Species Selection: Ensuring the appropriate selection and availability of native species can be a hurdle, especially in regions with limited biodiversity data or nursery resources.
- Maintenance and Protection: Although Miyawaki Forests are designed to be self-sustaining, they may require initial maintenance and protection from external factors such as vandalism or encroachment.
- Community Engagement: Educating and engaging local communities is crucial for the long-term success and stewardship of Miyawaki Forests, fostering a sense of ownership and environmental awareness.
Conclusion
Miyawaki Forests represent an innovative and sustainable approach to urban reforestation, offering a compact solution to address environmental challenges and promote biodiversity conservation. By leveraging the principles of native species selection, dense planting, and soil preparation, these forests can thrive and provide numerous ecological, social, and economic benefits to urban communities. As cities around the world strive to become more sustainable and resilient, the adoption of Miyawaki Forests presents a promising opportunity to create vibrant green spaces, mitigate climate change, and enhance the overall quality of life for urban dwellers.


Post a Comment