Introduction
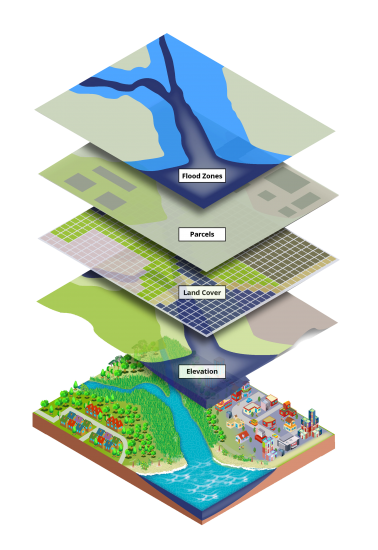
GIS, or Geographic Information System, is a robust technology that captures, analyzes, stores, and presents geographical and spatial data. This tool enables us to understand patterns and relationships within geographic information, transforming data into valuable insights. By merging data from diverse sources like satellite imagery, maps, and databases, GIS crafts layered visualizations called maps. These maps offer crucial insights for decision-making, problem-solving, and planning across fields like urban planning, environmental management, and disaster response.
Understanding GIS's Essence
GIS offers a digital framework to manage and analyze location-based data. It helps answer questions like "where," "what's nearby," and "what's changing over time." This technology shifts our spatial perspective, letting us make informed choices grounded in geographic context. From pinpointing optimal facility locations to tracking disease spread and assessing environmental impacts, GIS is pivotal in comprehending complex spatial relationships.
The Core of GIS Operation
- Data Collection: Gather geographic data using methods like satellite imaging, aerial photography, GPS surveys, and remote sensing.
- Data Storage: Store collected data in a spatial database, linked to geographic locations through coordinates (latitude and longitude).
- Data Integration: Unify various types of geographic data from different sources.
- Data Analysis: GIS's power lies here. Overlaying spatial data layers, GIS performs intricate analysis.
- Spatial Queries: Use GIS for specific spatial questions through queries.
- Geoprocessing: Manipulate spatial data for new info.
- Visualization: Present analyzed data as maps, graphs, charts, and reports.
- Decision Making: Insights from GIS guide decisions in various fields.
- Mapping: Fundamental to GIS, mapping displays data layers.
- Modeling: Advanced GIS involves spatial modeling.
Application of GIS
- 1. Urban Planning and Development: GIS helps urban planners analyze population distribution, land use patterns, and infrastructure needs. It aids in designing sustainable cities, optimizing transportation systems, and identifying suitable locations for new developments.
- 2. Environmental Management: GIS is essential for monitoring and managing natural resources, tracking changes in land cover, assessing environmental impacts, and preserving ecosystems. It supports initiatives such as conservation planning, watershed management, and pollution control.
- 3. Disaster Management: During emergencies and natural disasters, GIS assists in disaster response and recovery. It helps in mapping affected areas, identifying evacuation routes, and coordinating rescue efforts.
- 4. Public Health: GIS is used to analyze disease patterns, track the spread of illnesses, and identify potential health risks. It aids in healthcare planning, disease surveillance, and resource allocation for medical facilities.
- 5. Agriculture: Farmers use GIS to optimize crop management, plan irrigation systems, analyze soil conditions, and monitor crop health. It enables precision agriculture, reducing resource wastage and increasing productivity.
- 6. Transportation and Logistics: GIS supports transportation planning, route optimization, and traffic management. It's used by logistics companies to plan efficient delivery routes and monitor fleet movements.
- 7. Natural Resource Exploration: In industries like mining, oil and gas, and forestry, GIS helps in locating resources, assessing their potential, and managing extraction operations with minimal environmental impact.
- 8. Real Estate and Property Management: GIS assists in property valuation, land use analysis, and urban land management. It's used by real estate professionals to identify market trends and make informed investment decisions.
- 9. Criminal Justice and Law Enforcement: GIS aids law enforcement agencies in crime mapping, hotspot analysis, and resource allocation. It helps identify patterns and trends for more effective policing.
- 10. Tourism and Recreation: GIS enhances tourism planning by mapping attractions, trails, and amenities. It's used for creating interactive maps for tourists and promoting local destinations.
- 11. Archaeology and Cultural Heritage: GIS supports archaeological research by mapping archaeological sites, analyzing spatial relationships, and preserving cultural heritage.
- 12. Education and Research: GIS is used in academic and research settings to study geographical phenomena, conduct spatial analysis, and create educational resources.
- 13. Business Analysis: Companies use GIS for market analysis, site selection, and customer segmentation. It helps businesses understand spatial trends and make strategic decisions.
- 14. Government and Policy Making: Governments use GIS for land administration, infrastructure planning, and policy formulation. It assists in making informed decisions that impact communities.
GIS (Geographic Information System) has a wide range of applications across various fields due to its ability to analyze and visualize data in a geographic context. Some of the key uses and applications of GIS include:
Q&A
Question 1: What is GIS and how does it work?
Answer: GIS, or Geographic Information System, is a tool that helps us gather, study, and show information about places on the Earth's surface. Imagine it like a digital map that has different layers of information. This helps us see connections and things that might not be easy to understand in regular data. GIS works by bringing together data from various sources like satellite pictures and maps. It then creates useful maps that can answer questions like "Where do floods usually happen?" or "How far are schools from homes?" This helps people make smarter decisions, like where to build things or how to respond to emergencies.
Question 2: How is GIS used in real-life situations?
Answer: GIS finds use in many areas. For city planning, it helps design better roads and find good spots for new buildings. In nature, it helps keep track of things like forests and animal habitats. When disasters happen, it helps make maps of where help is needed. In health, GIS can show where diseases are spreading. It also helps farmers know how to grow crops well. Industries like mining use GIS to find things underground. In simple terms, GIS makes information about places more understandable and helps with making wise choices in many different fields.


Post a Comment