Size classification of soil
Soil is available in different sizes from small as 1 micron to big as 1 meter, shapes and different characteristics like porosity, strength etc. To understand the characteristics and uses of soil, classification is must needed.
Classifying the soil based on size is effective way to classify the different types of soil and know its aggregate properties.
Based on Indian Standard Soil Classification System (ISSCS), soil is classified into groups as Coarse, very coarse and fine, and further divided as shown in table below. The table confirms the classification of soil in which more than 50% material is satisfies the given size range. For ex, if more than 50% of soil is confirms size more than 0.075 mm or 75 microns, it is just aggregate classification of material.
|
Type of soil |
Size of particle |
||
|
Fine soil |
Clay (C) |
|
<0.002 mm |
|
Silt (M) |
|
0.002 – 0.075 mm |
|
|
Coarse soil |
Sand (S) |
Fine |
0.075 – 0.425 mm |
|
Medium |
0.425 – 0.200 mm |
||
|
Coarse |
0.200 – 4.750 mm |
||
|
Gravel (G) |
Fine |
4.750 – 20 mm |
|
|
Coarse |
20 – 80 mm |
||
|
Very coarse soil |
Cobble |
|
80 – 300 mm |
|
Boulder |
|
> 300 mm |
|
Table: IS soil classification system based on size of particle.
Clay, silt, sand and gravel are represented by symbols C, M, S and G respectively.
The size of soil is increasing as from clay to boulder, so the properties of soil is also varying with size range, for ex, soil particle < 0.002 mm Clay possess plasticity, while big size particles like 80 – 300 mm Cobble, or >300 mm boulders does not possess plasticity.
Same representation can be shown graphically as shown below.
|
< 0.002 mm |
0.200 – 0.075 mm |
0.075 – 0.425 mm |
0.425 – 0.200 mm |
0.200 – 4.750 mm |
4.750 – 20 mm |
20 – 80 mm |
80 – 300 mm |
> 300 mm |
|
|
|
Fine |
Medium |
Coarse |
Fine |
Coarse |
|
||
|
Clay |
Silt |
Sand |
Gravel |
Cobble |
Boulder |
||||
Figure: graphical representation of classification of soil based on size.
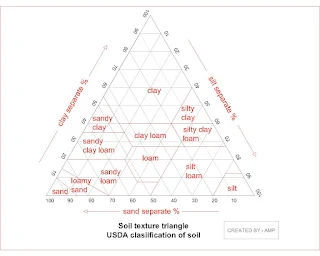
Based on USDA United States Department of Agriculture soil classification based on texture is represented by % separate of clay, silt and sand, as shown in figure below.
Figure : USDA classification of soil based on texture of soil.
Based on the amount of clay, sand and silt in %, we can classify soil using USDA soil classification triangle.

Post a Comment